Introduction
As businesses and governments race toward decarbonization and grid independence, commercial energy storage systems are becoming a cornerstone of modern energy strategy. Whether supporting renewable integration, reducing energy costs, or providing backup power, storage solutions are no longer optional — they are a critical investment.
This article explores the fundamentals of commercial energy storage, how it works, its cost implications, and where the global market is headed through 2025 and 2030.
What Is Commercial Energy Storage?
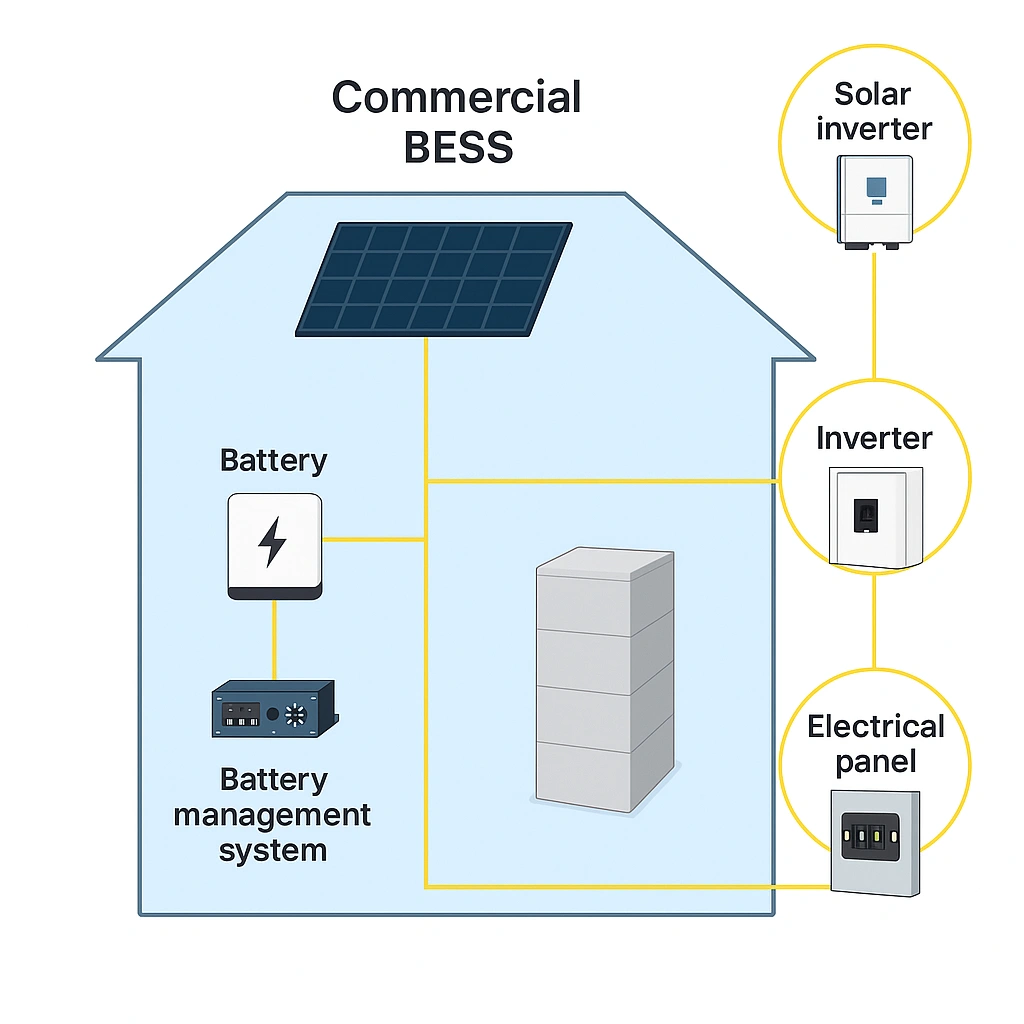
Commercial energy storage refers to the use of battery or other storage technologies by businesses, industrial facilities, utilities, or institutions to store electricity for later use. These systems help manage peak demand, reduce grid dependence, ensure power quality, and provide backup in case of outages.
Common setups include:
-
On-site battery banks for factories or office buildings
-
Microgrids for schools, hospitals, or data centers
-
Utility-scale storage paired with solar or wind farms
How Does Energy Storage Work?
At its core, energy storage involves capturing energy when supply exceeds demand and releasing it during periods of shortage.
In commercial systems, this typically means:
-
Charging batteries during off-peak hours or using solar/wind power
-
Storing the energy using technologies like lithium-ion, flow batteries, or sodium-ion
-
Discharging during peak demand, outages, or when grid prices spike
Storage systems can be standalone or integrated with generation sources like solar panels and diesel gensets.
What Is the Most Common Electricity Storage Method Today?
The dominant technology in commercial storage is the lithium-ion battery, particularly LiFePO₄ and NMC chemistries. These batteries offer:
-
High energy density
-
Fast response time
-
Modular scalability
Other emerging technologies include:
-
Flow batteries (suitable for long-duration applications)
-
Sodium-ion (gaining momentum for cost and cold-weather benefits)
-
Thermal and mechanical storage (less common for commercial sites)
What Is an Example of Commercial Energy?
A retail chain installing a 500 kWh battery system to offset peak-hour charges is one example. Another is a hospital using battery storage to maintain surgical operations during outages.
Key commercial sectors using storage:
-
Manufacturing plants
-
Hotels and resorts
-
Hospitals and healthcare campuses
-
Educational institutions
-
Data centers
Is Commercial Energy Cheaper Than Domestic?
Electricity for commercial and industrial customers is often billed differently than residential:
-
Time-of-use (TOU) rates and demand charges can cause spikes
-
Domestic users typically pay a flat per-kWh rate
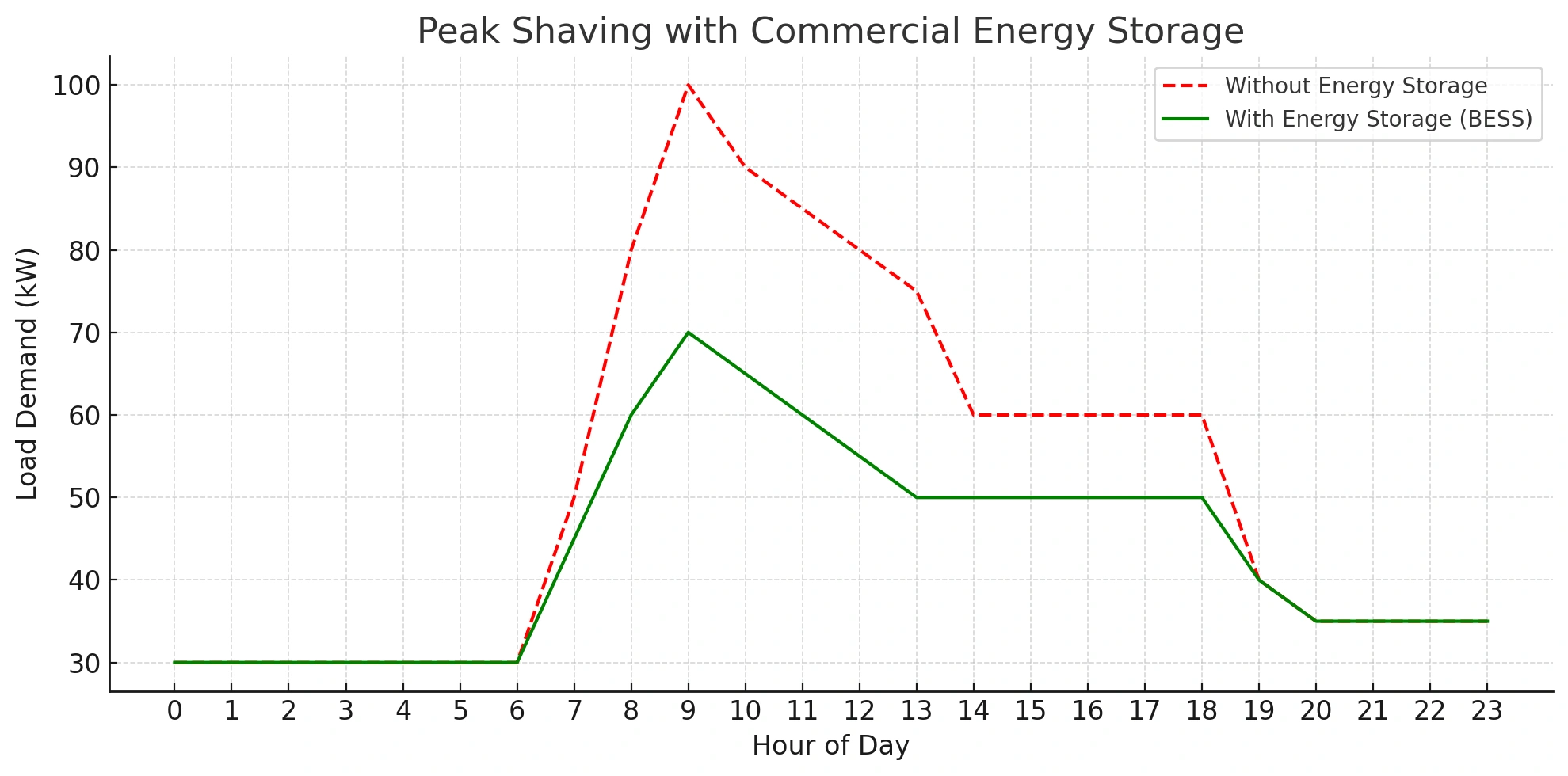
Energy storage allows businesses to shave peaks, avoid demand penalties, and maximize self-consumption, making commercial energy potentially cheaper when storage is deployed strategically.
Is Energy Storage Expensive?
Initial costs depend on the system size, chemistry, and use case:
| Capacity Range | Estimated Cost ($/Wh) | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 50–250 kWh | $0.195-0.222 | Small shops, clinics |
| 250–1000 kWh | $0.177-0.195 | Schools, hotels |
| 1 MWh+ | $0.167-0.177 | Factories, campuses |
However, the ROI comes from:
-
Reducing peak charges
-
Avoiding generator fuel costs
-
Participating in grid services (in some markets)
How Does Energy Storage Make Money?
Commercial energy storage can deliver ROI through several revenue and savings streams:
-
Peak shaving: reduce high-demand charges
-
Arbitrage: store during low-cost hours, discharge during high-cost hours
-
Backup power: avoid costly production halts
-
Grid services: frequency regulation, demand response (region-dependent)
-
Carbon credits & subsidies: applicable in the EU, US, and select Asian markets
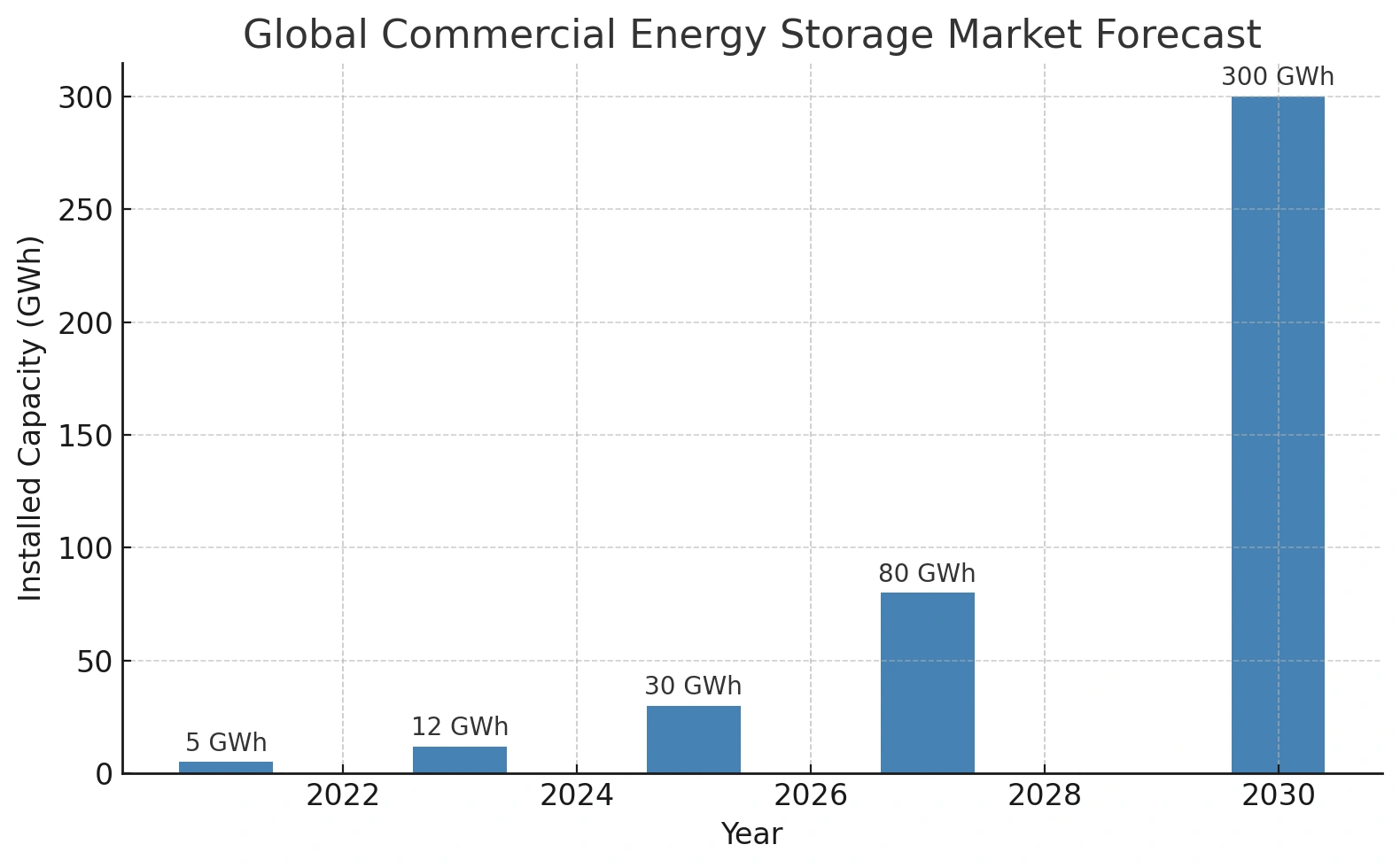
What Is the Energy Storage Market Outlook for 2025?
-
By 2025, the global commercial energy storage market is expected to:
-
Reach ~30 GWh in annual deployments (BloombergNEF)
-
See compound annual growth rates (CAGR) above 20% in Europe, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East
-
Be driven by lower battery costs and government mandates
China, Germany, the US, and the Gulf countries are emerging as growth hubs due to energy transition policies and grid modernization.
-
What Is the Energy Storage Forecast for 2030?
By 2030:
-
The market is projected to exceed 300 GWh/year in new installations
-
Modular BESS will become standard for factories, farms, and public institutions
-
AI-powered EMS (energy management systems) will dominate control platforms
-
Liquid-cooled and sodium-ion systems will gain share due to longevity and safety
Storage will shift from being a backup tool to an active energy management asset.
Conclusion
Commercial energy storage is no longer a “future” technology. It’s here — and growing fast. Businesses looking to secure energy independence, reduce operational risks, and cut costs should invest now, not later.
From small cafés to industrial parks, the right BESS (Battery Energy Storage System) ensures profitability, continuity, and resilience.
Need a tailored solution? Contact PKNERGY for full-service commercial energy storage planning, engineering, and deployment.
Save Money, Protect Environment
PKNERGY helps you reduce your energy bills for your home solar energy storage, store your solar energy for use anytime- at night or during an outage.