How long will the Powerwall battery last?
powwall battery life
These batteries typically last about 10 years, according to PKNERGY, a manufacturer of commercial solar cells for home use. This means that during the 20 to 30-year life cycle of the solar power generation facility, the battery energy storage system will most likely need to be replaced.
Typically, an energy storage system maintains more than 60% of its storage capacity over a 10-year period. Batteries must be operated between -10°C and 45°C to maintain warranty coverage.

According to reports, some time ago at 4 pm Eastern Time on the 14th, a large-scale power outage occurred in Manhattan, New York City, and then spread to parts of the eastern United States and Canada.
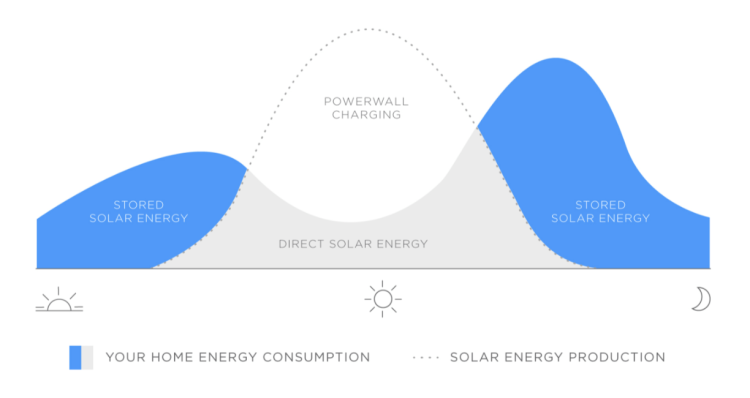
Houses using home solar systems are completely unaffected by power outages, and the energy stored in the solar system can still be used for normal life, including household appliances such as air conditioners, computers, washing machines, and refrigerators.
During the day when there is plenty of sunlight, the rooftop solar panels charge the Powerwall batteries, and when there is no sunlight at night, the batteries start to discharge for use in the room. The combination of these two devices can completely allow the homeowner to live a self-sufficient zero-emission life, and never have to pay the power company again.
Three factors mainly affect battery life
It turns out that a variety of factors can affect the lifespan of a residential battery storage system.
Battery life is mostly determined by usage cycles. Guaranteed to reach the 60% or 70% capacity threshold within a specific charge cycle, as evidenced by the PKNERGY Product Warranty.
In different usage environments, the life of the battery is not the same, humidity, high temperature, dust and other environments will shorten the life of the battery
According to the Faraday Institute, there are two usage scenarios that cause battery degradation: overcharging and trickle charging. Overcharging is the act of injecting current into a battery and charging it fully. Doing so can cause the battery to overheat and possibly catch fire.
Trickle charging is the process of continuously charging a battery to 100%. In this process, the battery capacity is inevitably lost, and this process will increase the internal temperature, thereby reducing capacity and life.
Another cause of degradation over time, the Faraday Institute notes, is the loss of lithium ions from the battery’s electrolyte. A side effect in a battery trap is the availability of free lithium, gradually reducing capacity.
While low temperatures can stop Li-ion batteries from functioning, they don’t actually degrade the battery’s performance or shorten its lifespan. According to the Faraday Institute, the overall lifespan of a battery is shortened at high temperatures. This is because the electrolyte between the electrodes decomposes at high temperatures, causing the battery to lose its ability to flow lithium ions. This reduces the number of lithium ions the electrode can accept into its structure, draining the capacity of the lithium-ion battery.
maintain
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) recommends that home users install batteries in a cool, dry location, preferably a garage, to minimize the impact of a fire. The battery and its surrounding components deserve adequate cooling, while regular maintenance checks help ensure optimal operation.
Try to avoid repeated deep discharge of the battery, because the more discharge, the shorter the life. If your residential battery storage system is discharging heavily every day, it’s time to add a battery pack.
The batteries connected in series should maintain the same charge, although the battery pack may display a total charge of 24V, there may be a voltage difference between the batteries, which is not conducive to protecting the long-term operation of the battery energy storage system. In addition, it is recommended to set the correct voltage set point for the charger and charge controller as specified by the battery manufacturer.
Operation and maintenance personnel should check frequently. Things to check for include leaks (buildup on the outside of the battery) and consistent voltage.



