Understanding the Difference Between Low Voltage and High Voltage Home Energy Storage Systems
🏠 A Practical Guide for Homeowners Seeking Reliable, Scalable Solar Energy Storage
As solar adoption accelerates worldwide, homeowners are turning to home energy storage systems (ESS) to maximize self-consumption, gain grid independence, and ensure backup power during outages. One of the first decisions you’ll face is whether to install a low voltage (LV) or high voltage (HV) system. This guide explains the technical and practical differences between them — and helps you choose the best fit for your home.
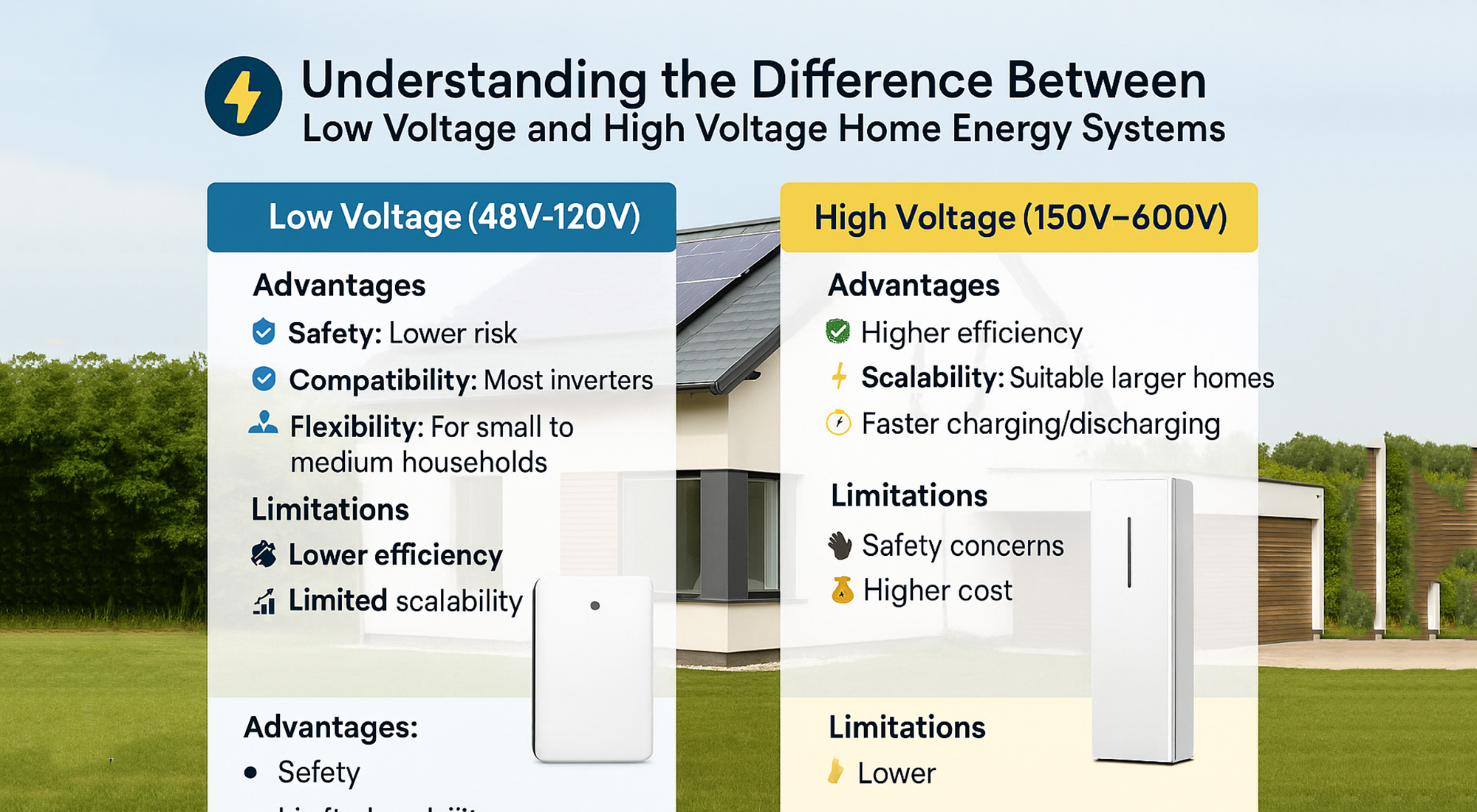
🔋 What Is a Low Voltage Home ESS?
A low voltage system typically operates between 48V and 120V, using LiFePO₄ batteries known for safety and longevity. These modular systems are popular for their affordability and ease of installation, making them ideal for off-grid homes or cabins.
✅ Advantages of Low Voltage Systems
- 🛡️ Safety: Lower voltage reduces shock risk during installation or maintenance.
- 🔌 Compatibility: Works seamlessly with most hybrid and off-grid inverters.
- 🏡 Flexibility: Perfect for small to medium households or backup-only setups.
⚠️ Limitations
- ⚙️ Lower efficiency due to higher current flow.
- 📉 Limited scalability for larger homes with higher consumption.
⚡ What Is a High Voltage Home ESS?
High voltage systems generally operate from 150V to 600V and are ideal for grid-tied or hybrid setups with high energy demand. They often pair with advanced solar inverters for superior performance and faster charge/discharge cycles.
✅ Advantages of High Voltage Systems
- ⚡ Higher efficiency: Lower transmission losses thanks to lower current.
- 🚀 Scalability: Easily expands for villas and smart homes.
- ⏱️ Faster charging/discharging: Supports dynamic energy profiles and EV integration.
⚠️ Limitations
- 🧤 Requires trained installers for safety compliance.
- 💰 Slightly higher upfront system and installation cost.
📊 Application Scenarios
| Use Case | Recommended System |
|---|---|
| 🏕️ Small off-grid cabin | Low Voltage ESS |
| 🏠 Urban home with rooftop solar | High Voltage ESS |
| 💡 Energy backup only | Low Voltage ESS |
| 🚗 Smart home with EV charger | High Voltage ESS |
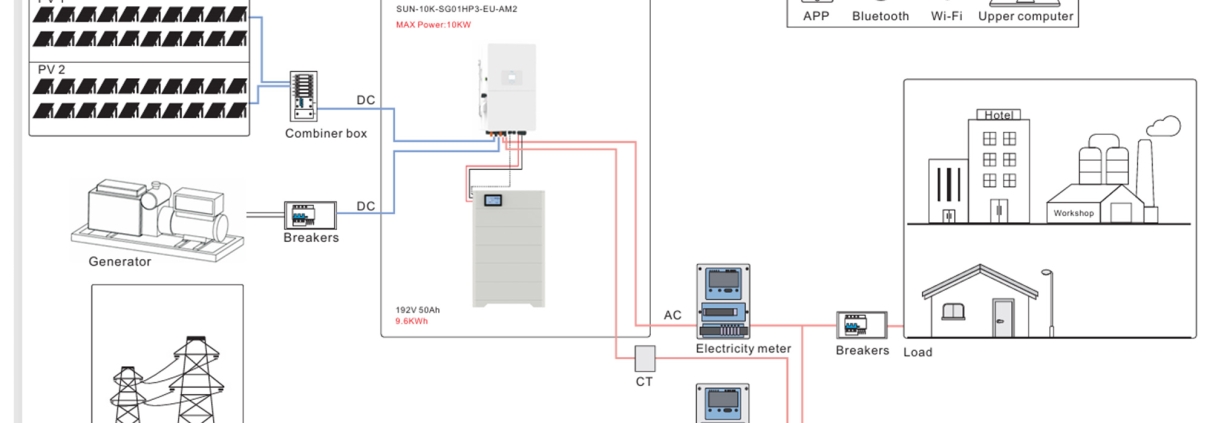
⚙️ Installation & Inverter Considerations
When deciding between LV and HV, pay attention to the inverter. Not all inverters support both voltage types. High-voltage systems often require transformerless hybrid inverters for best efficiency and safety integration.
🌍 PKNERGY Home ESS Recommendations
- 🏡 5kWh Wall-Mount 48V ESS — Best for entry-level users
- 🔋 15kWh High Voltage System — For large homes and villas
- ⚙️ Rack-Mount ESS Cabinets — Scalable and modular for hybrid use
✅ Conclusion
Both low voltage and high voltage ESS architectures have their place in home energy management. The best choice depends on your usage, inverter compatibility, and long-term expansion goals. Whether you need a simple backup or a full smart-home solution, PKNERGY provides tailored systems to match your energy future.
👉 Contact PKNERGY today to find the right ESS for your home and enjoy uninterrupted, efficient, and scalable solar storage.
📩 Contact Information
Cassie | PKNERGY Energy Co., Ltd.
Email: sale4@pknergy.com
WhatsApp/Tel: +86 13974604556
🌐 Website: https://pknergypower.com